Diabetic nephropathy is a type of kidney disease that results from long-term high blood sugar levels. Over time, the high glucose levels in the blood can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. This can lead to kidney failure if not managed appropriately.
What Causes Diabetic Nephropathy?
The primary cause of diabetic nephropathy is prolonged hyperglycemia, where high blood sugar levels persist over time. This chronic exposure to glucose can lead to inflammation and scarring of the kidney tissues. The kidneys’ filtering units, called nephrons, become damaged, resulting in a decreased ability to filter blood effectively. This progressive damage can eventually lead to kidney failure if left unchecked.
The Stages of Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy progresses through several stages, each characterized by different levels of kidney function and damage. In the early stages, microalbuminuria may occur, where small amounts of protein leak into the urine. As the disease progresses, proteinuria becomes more evident, indicating significant kidney damage. Eventually, if not managed, it can lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
The Impact of Diabetic Nephropathy on Overall Health
Beyond affecting kidney function, diabetic nephropathy can have systemic effects on overall health. The buildup of waste products and excess fluids can lead to complications such as hypertension, heart disease, and neuropathy. Moreover, the emotional and financial burden of managing diabetic nephropathy can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, underscoring the importance of prevention and early intervention.
Symptoms of Diabetic Nephropathy
In the early stages, diabetic nephropathy often presents no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the hands, feet, or face (edema)
- Fatigue or feeling tired
- Nausea or vomiting
- Trouble sleeping or concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- High blood pressure
Recognizing these signs early and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for effective management and treatment.
Early Signs to Watch For
In the initial phases, signs of kidney damage might not be apparent, which is why regular screenings are vital for those with diabetes. Subtle changes such as increased urinary protein levels can be an early indicator. These signs often go unnoticed without specific testing, highlighting the importance of routine medical check-ups to catch any early signs of kidney impairment.
Why Symptoms Can Be Overlooked
The symptoms of diabetic nephropathy can often overlap with other health issues, making them easy to overlook. Fatigue and high blood pressure, for example, are common in many conditions. This overlap can delay diagnosis and treatment, which is why healthcare professionals emphasize vigilance and regular monitoring for those at risk.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Timely consultation with a healthcare provider is critical when symptoms are present. Healthcare professionals can perform diagnostic tests such as blood and urine tests to assess kidney function. Early diagnosis allows for intervention strategies that can slow the progression of the disease and improve patient outcomes significantly.
The Connection Between Kidney Disease and Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease. The condition develops when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels and filtering units in the kidneys. This damage impairs the kidneys’ ability to function properly, leading to an accumulation of waste products and fluids in the body.
The Biological Mechanism Linking Diabetes to Kidney Disease
The link between diabetes and kidney disease is primarily due to the impact of high blood sugar on the blood vessels within the kidneys. Elevated glucose levels can cause these vessels to become thickened and scarred, reducing their ability to filter blood effectively. Additionally, diabetes can increase blood pressure, further straining the kidneys and exacerbating damage over time.
The Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a common feature of type 2 diabetes, plays a significant role in the development of diabetic nephropathy. When the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, blood sugar levels rise, leading to increased demand on the kidneys to filter excess glucose. This persistent high workload can accelerate kidney damage and contribute to the progression of nephropathy.
How Diabetes-Related Inflammation Affects the Kidneys
Chronic inflammation is another mechanism through which diabetes can lead to kidney damage. High blood sugar levels can trigger an inflammatory response within the kidneys, causing cellular damage and fibrosis. Over time, this inflammation can reduce kidney function, underscoring the importance of managing blood sugar and inflammation to protect renal health.
Risk Factors for Developing Diabetic Nephropathy
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy, including:
- Poor blood sugar control
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol levels
- Family history of kidney disease
- Being of African American, Hispanic, or Native American descent
Managing these risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing diabetic nephropathy.
To better understand how diabetes can lead to serious kidney complications, read more about the link between diabetes and kidney failure.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics can play a significant role in an individual’s risk for developing diabetic nephropathy. Studies have shown that those with a family history of kidney disease are more susceptible to developing it themselves. Genetic variations can influence how the body handles glucose and blood pressure, impacting kidney health over time.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, significantly impact the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. A sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits can lead to obesity, which increases the risk of both diabetes and kidney disease. Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins, can also contribute to kidney damage.
The Influence of Coexisting Medical Conditions
Other medical conditions, such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome, can exacerbate the risk of diabetic nephropathy. These conditions often contribute to hypertension and poor blood sugar control, accelerating kidney damage. Integrated management of these coexisting conditions is crucial for reducing the overall risk of nephropathy.
Preventing Diabetic Nephropathy
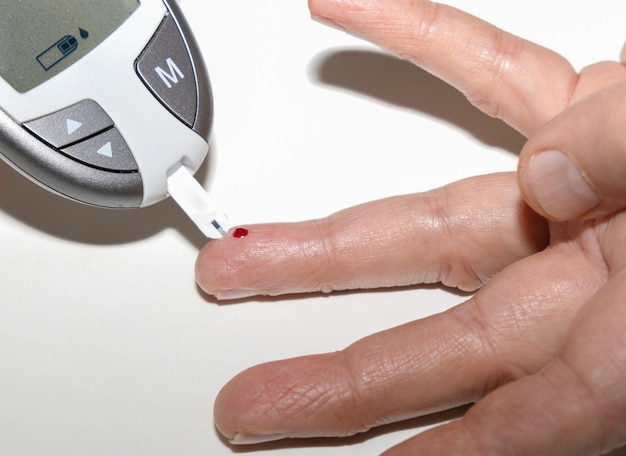

Preventing diabetic nephropathy involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical management. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
Maintain Optimal Blood Sugar Levels
Keeping your blood sugar levels within the target range is crucial. This can be achieved through:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels
- Adhering to a diabetes-friendly diet
- Taking medications as prescribed
- Engaging in regular physical activity
Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for preventing diabetic nephropathy. By keeping track of glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. This proactive approach helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of kidney damage.
Dietary Strategies for Blood Sugar Control
A diabetes-friendly diet is central to managing blood sugar levels. Emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Reducing the intake of refined sugars and processed foods is equally important in preventing spikes in glucose levels that can harm the kidneys.
The Role of Medication in Blood Sugar Management
For many individuals with diabetes, medication is a necessary component of managing blood sugar levels. Insulin and oral diabetes medications can be effective in maintaining glucose within a healthy range. It’s vital to follow healthcare provider recommendations regarding medication to prevent kidney complications.
Control Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can exacerbate kidney damage. To manage blood pressure, consider:
- Reducing salt intake
- Regular exercise
- Stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation
- Medication if prescribed by your doctor
Salt Reduction and Its Effects
Reducing salt intake is one of the most effective ways to manage blood pressure. High sodium levels can lead to increased fluid retention, raising blood pressure and straining the kidneys. Adopting a low-sodium diet can significantly lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of kidney damage.
Exercise as a Blood Pressure Management Tool
Regular physical activity is a powerful tool for managing blood pressure. Exercise helps improve cardiovascular health, reduce stress, and promote weight loss, all of which contribute to lower blood pressure. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial for kidney health.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can contribute to elevated blood pressure, making stress management techniques vital for kidney health. Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels. Incorporating these techniques into daily life can have a positive impact on both blood pressure and overall well-being.
Adopt a Kidney-Friendly Diet
A balanced diet is essential for kidney health. Focus on:
- Consuming fruits and vegetables
- Reducing saturated fats and processed foods
- Limiting protein intake, as advised by a healthcare professional
- Staying hydrated but not overhydrating
The Role of Antioxidants
Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, which can protect the kidneys from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a contributor to kidney damage, and a diet high in antioxidants can help mitigate its effects. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables can enhance kidney health.
Importance of Protein Moderation
While protein is an essential nutrient, excessive intake can strain the kidneys. Those with diabetes should consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate level of protein intake. Moderating protein consumption can help reduce the risk of further kidney damage.
Hydration: Finding the Balance
Staying hydrated is crucial for kidney function, but overhydration can also be harmful. Drinking adequate amounts of water helps the kidneys filter waste efficiently. However, it’s important to find a balance and avoid excessive fluid intake, which can lead to complications such as swelling and high blood pressure.
Quit Smoking
Smoking can accelerate kidney damage and worsen diabetes complications. Quitting smoking is one of the most beneficial steps you can take for your kidney health and overall well-being.
The Impact of Smoking on Kidney Health
Smoking has a direct impact on blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the kidneys. This diminished circulation can exacerbate kidney damage and increase the risk of nephropathy. Quitting smoking can improve blood vessel health and reduce the progression of kidney disease.
Smoking Cessation Strategies
Successfully quitting smoking often requires a multi-faceted approach. Behavioral therapies, nicotine replacement products, and support groups can be effective tools. Working with healthcare professionals can provide personalized strategies to overcome nicotine addiction and protect kidney health.
Long-Term Benefits of Quitting Smoking
The benefits of quitting smoking extend beyond kidney health. Smoking cessation reduces the risk of heart disease, lung cancer, and other chronic conditions. The positive effects on overall health and well-being make quitting smoking a worthwhile investment in one’s future.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular visits to your healthcare provider for check-ups and kidney function tests are crucial. Early detection of any changes in kidney function can lead to timely interventions and better outcomes.
The Importance of Routine Screenings
Routine screenings for kidney function, such as urine tests and blood tests, are vital for early detection of nephropathy. These tests can identify changes in kidney function before symptoms become apparent. Early detection allows for timely intervention and better management of the condition.
Building a Collaborative Healthcare Team
Building a collaborative healthcare team is essential for managing diabetes and preventing nephropathy. This team typically includes a primary care physician, endocrinologist, nephrologist, and dietitian. Regular communication with healthcare providers ensures comprehensive care and helps patients stay on track with their management plan.
Personal Health Tracking and Monitoring
In addition to regular check-ups, personal health tracking can empower individuals to manage their condition. Using tools such as glucose monitors, blood pressure cuffs, and health apps can provide valuable insights into daily health metrics. This proactive approach can aid in early detection and management of potential complications.
Diabetic Nephropathy Treatment Options
If diabetic nephropathy is diagnosed, several treatment options are available to slow its progression and manage symptoms:
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to control blood pressure, manage blood sugar levels, and reduce protein loss in the urine. Common medications include:
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs for blood pressure control
- SGLT2 inhibitors for blood sugar management
- Diuretics to help with fluid retention
The Role of ACE Inhibitors and ARBs
ACE inhibitors and ARBs are commonly used to manage blood pressure in individuals with diabetic nephropathy. These medications work by relaxing blood vessels, reducing the workload on the kidneys. By controlling blood pressure, they help slow the progression of kidney damage.
SGLT2 Inhibitors and Their Benefits
SGLT2 inhibitors are a newer class of medications that can benefit individuals with diabetic nephropathy. These drugs help lower blood sugar levels and have been shown to reduce the risk of kidney disease progression. They work by preventing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, promoting excretion in the urine.
Managing Fluid Retention with Diuretics
Diuretics, also known as water pills, help manage fluid retention in individuals with nephropathy. By promoting urine production, diuretics reduce fluid buildup in the body, alleviating symptoms such as swelling and high blood pressure. They are an important component of managing advanced kidney disease.
Dialysis
In advanced cases, when kidney function is severely impaired, dialysis may be necessary. Dialysis is a procedure that helps remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys can no longer do so effectively.
Types of Dialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis
There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis involves filtering blood through a machine, while peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of the abdomen to filter blood internally. The choice between these methods depends on individual health needs and lifestyle preferences.
Preparing for Dialysis Treatment
Preparing for dialysis involves several considerations, including the placement of a vascular access point for hemodialysis or the insertion of a catheter for peritoneal dialysis. Patients may need to make lifestyle adjustments, such as altering their diet and schedule, to accommodate dialysis sessions. Education and support from healthcare providers can ease this transition.
Living with Dialysis: Lifestyle and Support
Living with dialysis requires adjustments to daily life, including dietary changes and regular treatment sessions. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups can help patients manage these changes. Maintaining a positive outlook and seeking emotional support are crucial for adapting to life with dialysis.
Kidney Transplant
For some individuals, a kidney transplant may be the best option. This involves receiving a healthy kidney from a donor to replace the function of the damaged kidneys.
The Process of Kidney Transplantation
The kidney transplant process involves several stages, including evaluation, finding a donor, and undergoing surgery. After the transplant, patients require lifelong immunosuppressive medication to prevent organ rejection. The procedure offers the potential for improved quality of life and freedom from dialysis.
Finding a Suitable Donor
Finding a suitable kidney donor can be a challenging process. Donors can be living or deceased, and compatibility testing is crucial to ensure a successful transplant. Some patients may wait on transplant lists, while others may find a match through living donations from family or friends.
Post-Transplant Care and Monitoring
Post-transplant care is essential for long-term success. Patients must adhere to a strict medication regimen and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor kidney function and overall health. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress, are also important for transplant recipients.
More about diabetic nephropathy from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Final Thoughts on Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that requires attention and proactive management. By maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, controlling blood sugar and blood pressure, and working closely with healthcare professionals, the risks of developing diabetic nephropathy can be minimized.
The Importance of Awareness and Education
Awareness and education are key components in preventing diabetic nephropathy. Understanding the risks and symptoms empowers individuals to take proactive steps to protect their kidney health. Educational resources and support from healthcare professionals can guide patients in managing their condition effectively.
Empowerment Through Self-Management
Empowering individuals with diabetes to take charge of their health is crucial for preventing complications like nephropathy. Self-management involves making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adherence. By taking an active role in their health, individuals can reduce their risk of kidney damage and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Support Systems
Support systems play a vital role in managing diabetic nephropathy. Family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide encouragement and assistance in adhering to lifestyle changes and treatment plans. Building a strong support network can enhance motivation and resilience in managing diabetes and its complications.
Remember, early detection and intervention are key. Regular check-ups and being vigilant about any symptoms can make a significant difference in managing diabetic nephropathy effectively. Taking these steps not only helps protect your kidneys but also enhances your overall health and quality of life.

