Kidney disease refers to any condition that affects the kidneys’ ability to filter waste from the blood. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining overall health by filtering out toxins, balancing electrolytes, and regulating blood pressure. When kidneys are damaged, they cannot perform these functions effectively, leading to a buildup of waste in the body.
The Role of the Kidneys in the Body
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located in the lower back. They are essential for filtering blood, removing waste products, and balancing fluids. Each day, the kidneys filter approximately 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce about 1 to 2 quarts of urine. This process is vital for maintaining the body’s internal equilibrium, ensuring that electrolytes like sodium and potassium are in balance, and eliminating excess substances that can be harmful.
Types of Kidney Disease
There are several types of kidney disease, each with unique causes and characteristics. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose function. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a sudden and temporary loss of kidney function, often due to an illness or injury. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that leads to the formation of cysts in the kidneys, impairing their function. Identifying the type of kidney disease is essential for determining the most effective treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Various factors can contribute to kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the leading causes, accounting for nearly two-thirds of cases. Other risk factors include a family history of kidney disease, age, obesity, smoking, and certain medications. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention. By addressing modifiable risks, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their kidney health.
Common Symptoms of Kidney Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of kidney disease early can help in managing the condition before it progresses. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in ankles, feet, or hands
- Changes in urination frequency or appearance
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent itching
- Muscle cramps
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of kidney disease and occur due to the buildup of toxins and impurities in the blood. When the kidneys fail to function properly, waste products accumulate, leading to feelings of tiredness and a decrease in energy levels. This can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Swelling and Fluid Retention
Swelling, also known as edema, particularly in the ankles, feet, and hands, is a telltale sign of kidney disease. The kidneys regulate fluid balance, and when they are not functioning correctly, excess fluid can accumulate in the body. This results in noticeable swelling, which can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful.
Changes in Urination
Alterations in urination patterns, such as increased frequency, urgency, or changes in color and appearance, can indicate kidney issues. Individuals may notice foamy urine, which suggests the presence of protein, a sign of kidney damage. Monitoring these changes and reporting them to a healthcare provider is essential for early intervention.
Shortness of Breath and Respiratory Issues
Shortness of breath can occur as a result of fluid buildup in the lungs due to kidney dysfunction. When the kidneys are unable to remove excess fluid, it can accumulate in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. This symptom requires immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
Persistent Itching and Skin Changes
Persistent itching is often a result of the buildup of waste products in the blood, which can irritate the skin. This symptom can be distressing and lead to skin damage from scratching. Managing itching through medical treatment and skincare can improve comfort and quality of life.
Muscle Cramps and Electrolyte Imbalance
Muscle cramps, particularly in the legs, can occur due to an imbalance of electrolytes like calcium and phosphorus. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of these minerals, and their dysfunction can lead to painful cramping. Proper management through diet and medication can alleviate this symptom.
How Does Kidney Disease Cause Hypertension?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common consequence of kidney disease. But how does this happen? The kidneys are responsible for regulating blood pressure by controlling the volume of blood (via fluid removal) and releasing hormones that manage blood pressure levels.
The Mechanism of Blood Pressure Regulation
The kidneys influence blood pressure through a complex system involving fluid balance and hormone secretion. They adjust the amount of fluid in the bloodstream by filtering excess sodium and water, which affects blood volume and pressure. Additionally, the kidneys produce renin, an enzyme that plays a key role in regulating blood pressure by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure.
Impact of Impaired Kidney Function on Blood Pressure
When kidney function is impaired, this regulation is disrupted, leading to increased blood pressure. The inability to remove excess fluid causes blood volume to rise, putting extra pressure on blood vessels. Moreover, damaged kidneys may overproduce renin, exacerbating hypertension. This creates a feedback loop where high blood pressure further damages the kidneys, worsening the condition.
The Vicious Cycle of Kidney Disease and Hypertension
The relationship between kidney disease and hypertension is cyclical. High blood pressure can damage the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to function effectively. This damage leads to further deterioration of kidney function, which in turn exacerbates hypertension. Breaking this cycle requires a comprehensive approach to manage both conditions simultaneously.
Hypertension and Its Impact on Kidney Function
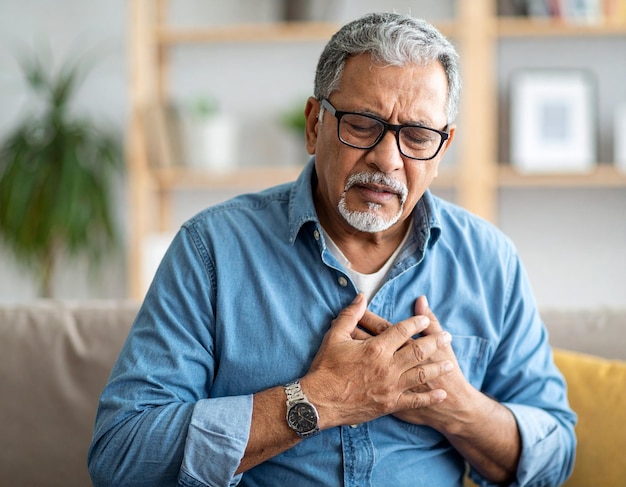

High blood pressure can have a detrimental effect on kidney function. Over time, the increased pressure can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste effectively. This damage can lead to further deterioration of kidney function, increasing the risk of chronic kidney disease.
How Hypertension Damages the Kidneys
High blood pressure exerts excessive force on the walls of blood vessels, including those in the kidneys. This can lead to the thickening and narrowing of these vessels, reducing blood flow and impairing kidney function. Over time, this damage can cause scarring (glomerulosclerosis) and kidney tissue loss, ultimately resulting in chronic kidney disease.
Long-Term Consequences of Uncontrolled Hypertension
If hypertension remains uncontrolled, it can lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where the kidneys lose nearly all their function. This stage requires dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival. Uncontrolled high blood pressure is also a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke, further complicating the individual’s health status.
Recognizing High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure often has no symptoms, which is why it’s often referred to as the “silent killer.” Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial, especially if you have a family history of hypertension or kidney disease. Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mmHg. Readings consistently above this range may indicate hypertension, requiring medical attention.
The Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular blood pressure checks are essential for early detection and management of hypertension. Home monitoring devices can provide valuable information between doctor visits, allowing individuals to track their progress and identify trends. Keeping a record of blood pressure readings can aid healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure readings consist of two numbers: systolic and diastolic. The systolic pressure, the higher number, measures the force of blood against artery walls during heartbeats. The diastolic pressure, the lower number, measures the force between beats. Understanding these readings can help individuals recognize when their blood pressure is within a healthy range or if medical intervention is needed.
Risk Factors for Developing Hypertension
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing hypertension, including age, genetics, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, high sodium intake, and stress. Identifying and addressing these factors through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment can significantly reduce the risk of hypertension and its associated complications.
The Role of Specialists in Managing Kidney and Hypertension Issues

Kidney and hypertension specialists, such as nephrologists and cardiologists, play a vital role in managing these interconnected conditions. They can provide tailored treatment plans that address both kidney function and blood pressure control. This might include medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to prevent the progression of disease.
The Expertise of Nephrologists
Nephrologists are medical doctors specializing in kidney care and treating kidney-related diseases. They possess the expertise to diagnose and manage kidney disease, offering personalized treatment plans that may include medications, dietary recommendations, and, in severe cases, dialysis. Their role is crucial in preventing the progression of kidney disease and managing its complications.
The Role of Cardiologists
Cardiologists specialize in heart and blood vessel health, making them essential in managing hypertension, particularly when it affects kidney function. They can prescribe antihypertensive medications, recommend lifestyle changes, and perform procedures to improve cardiovascular health. Collaboration between cardiologists and nephrologists ensures a comprehensive approach to treating both conditions.
Treatment Approaches
Managing kidney disease and hypertension often requires a comprehensive approach:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe antihypertensive drugs to control blood pressure. In cases of kidney disease, medications that protect kidney function are also essential.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet and exercise play a significant role. Reducing salt intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage both conditions.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine monitoring of kidney function and blood pressure is crucial to detect any changes early and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Medications for Blood Pressure Control
Medications such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), and diuretics are commonly prescribed to control blood pressure. These medications help relax blood vessels, reduce fluid buildup, and protect the kidneys from further damage. A healthcare provider can determine the most suitable medication based on the individual’s health status and specific needs.
Lifestyle Changes for Kidney and Blood Pressure Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is a cornerstone of managing kidney disease and hypertension. A balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can support kidney function and blood pressure control. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces stress, further benefiting heart and kidney health.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for managing kidney disease and hypertension effectively. These visits allow for the assessment of kidney function through blood and urine tests and the monitoring of blood pressure. Early detection of changes enables timely adjustments to treatment plans, preventing complications and improving long-term outcomes.
Specialized Kidney and Hypertension Care with Kidney MD
To complement the blog on Understanding the Link Between Kidney Disease and Hypertension, it’s important to highlight how specialized care can make all the difference. Kidney MD offers comprehensive nephrology services designed to diagnose, manage, and treat kidney-related conditions and their underlying causes, such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Their patient-centered approach ensures that each individual receives a personalized care plan tailored to their specific needs, helping them manage chronic kidney disease, electrolyte imbalances, and associated complications with confidence and clarity.
At Kidney MD, services go beyond diagnosis. The clinic provides continuous monitoring of kidney function, blood pressure, and lab values to ensure early detection of any changes in the patient’s condition. Their expert team includes board-certified nephrologists who are experienced in managing complex kidney issues and preventing progression to end-stage renal disease. Whether a patient is dealing with early-stage chronic kidney disease or preparing for dialysis, Kidney MD ensures ongoing support and education to improve health outcomes.
What sets Kidney MD apart is their focus on patient education and collaborative care. They work closely with primary care physicians, cardiologists, and other specialists to provide a holistic approach to health. From nutritional counseling to medication management and preparation for kidney transplant evaluations, Kidney MD ensures that patients and their families are empowered every step of the way.
👉 Learn more about how high blood pressure affects the kidneys from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/high-blood-pressure
Preventing Kidney Disease and Hypertension
While some risk factors for kidney disease and hypertension, such as genetics, cannot be changed, others can be managed through lifestyle choices.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit salt and processed foods.
- Stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Limit Alcohol and Tobacco: Reducing alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can significantly benefit kidney and heart health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports kidney function and helps maintain a healthy blood pressure.
The Impact of Diet on Kidney and Cardiovascular Health
Diet plays a crucial role in preventing kidney disease and hypertension. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients while limiting sodium, which can help control blood pressure and reduce kidney strain. Processed foods, often high in salt and unhealthy fats, should be minimized to support overall health.
The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight. Exercise also reduces stress, a known risk factor for hypertension. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, and cycling are effective in promoting cardiovascular and kidney health. Establishing a consistent exercise routine can lead to lasting health benefits.
The Importance of Avoiding Harmful Substances
Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco use are critical steps in preventing kidney disease and hypertension. Excessive alcohol can raise blood pressure, while smoking damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Making the choice to avoid these substances can significantly improve long-term health outcomes.
The Role of Hydration in Kidney Health
Staying adequately hydrated is essential for kidney function. Water helps flush out toxins and waste products, reducing the risk of kidney stones and infections. Adequate hydration also supports healthy blood pressure levels. While individual water needs vary, aiming for at least eight glasses of water a day is a good starting point for maintaining kidney health.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between kidney disease and hypertension is crucial for preventing and managing these conditions effectively. By recognizing symptoms early, consulting with specialists, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can protect your kidneys and maintain good cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups and proactive management are key to reducing the risk of complications and ensuring a better quality of life.
Importance of Early Intervention
Recognizing and addressing symptoms of kidney disease and hypertension early is vital for successful management. Early intervention can slow the progression of kidney damage, control blood pressure, and prevent complications. Healthcare providers play a critical role in guiding patients through diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications to improve outcomes.
The Role of Patient Education and Support
Educating patients about kidney disease and hypertension empowers them to take control of their health. Understanding the conditions, treatment options, and lifestyle changes fosters informed decision-making and adherence to care plans. Support from healthcare providers, family, and support groups can enhance motivation and encourage long-term commitment to health.
Encouragement for Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine health check-ups are essential for monitoring kidney function and blood pressure, detecting changes early, and adjusting treatment plans as needed. Regular visits to healthcare providers offer opportunities for patients to discuss concerns, receive guidance, and track their progress. Prioritizing regular check-ups can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Remember, if you suspect you have symptoms of kidney disease or high blood pressure, seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes.